Software Development
It typically begins with requirement gathering and analysis, where developers understand the client’s needs. This is followed by system design, programming, coding, and testing to ensure the software meets quality standards. After testing, the software is deployed and maintained. This lifecycle is crucial for delivering a reliable and efficient software product.
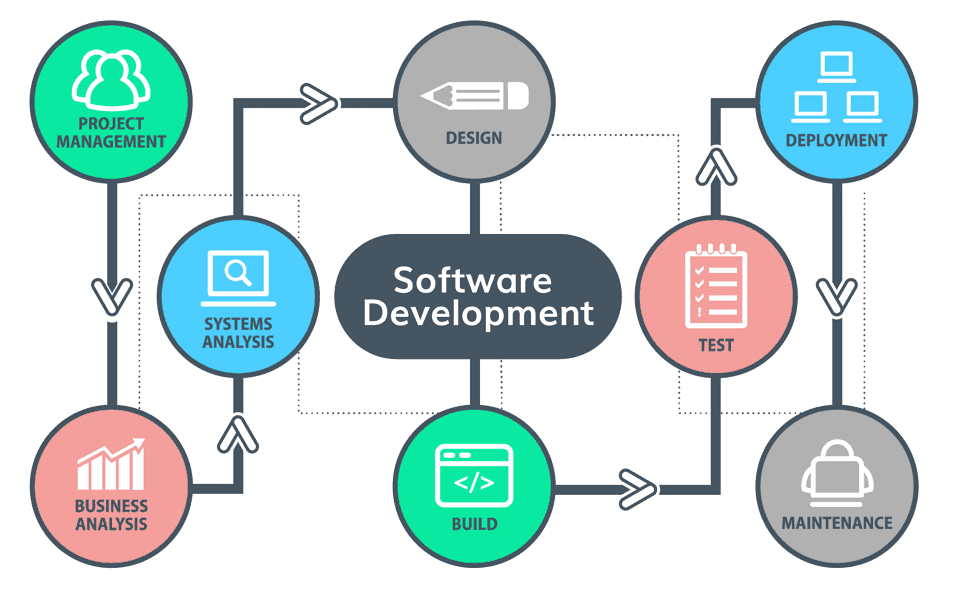
Process
- The software development process is a structured sequence of stages that teams follow to create a software product.
- It typically begins with requirement gathering and analysis, where developers understand the client’s needs.
- This is followed by system design, programming, coding, and testing to ensure the software meets quality standards.
- After testing, the software is deployed and maintained.
- This lifecycle is crucial for delivering a reliable and efficient software product.
Advantages
- Software development offers numerous advantages, such as the ability to create custom solutions tailored to specific operational & functional business needs.
- It enhances efficiency and productivity by automating tasks and processes. The continuous evolution of technology ensures that software development remains a critical and valued skill in the modern economy.
Our offerings
PLC Logic Development
⮚ Understanding of application, development of PLC programming in accordance with ISA S88 Standards for Batch Process Design, IEC 61508 / IEC 61511 Safety standard, IEC 61131-3 Programming for various type of pharma process machines, plants, critical, manufacturing process, batch processes and ensure the reliability robustness and flexibility in controlling various types of equipment and processes.
⮚ The development of PLC programming within the pharmaceutical industry is a critical task that requires adherence to various international standards to ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency. Standards such as ISA S88 provide guidelines for batch process design, while IEC 61508 and IEC 61511 outline the safety requirements for electrical, electronic, and programmable electronic systems.
⮚ Additionally, IEC 61131-3 offers a framework for programming languages used in PLCs, ensuring that programs are robust and flexible enough to manage the complex operations of pharma process machines and plants effectively.
⮚ These standards collectively contribute to the high-quality manufacturing processes necessary in the pharmaceutical sector and other industries.
MES, Historian and Real Time Portal Engineering
⮚ Key functions include production scheduling, resource allocation, quality management, and data collection.
⮚ MES ensures real-time visibility into manufacturing processes, enabling better decision-making.
⮚ A historian is a specialized database used to store time-series data from industrial processes.
⮚ IIt collects and archives data at high frequencies (e.g., sensor readings, process variables) for analysis and reporting.
⮚ Historians enable trend analysis, performance monitoring, and predictive maintenance
Data Collection & Integration
⮚ Understanding customer requirements is a critical first step in data collection and integration. By utilizing a variety of sources such as sensors, IoT devices, and machinery, a comprehensive dataset can be assembled. Integrating this data effectively allows for a unified view, providing valuable insights that can drive informed decision-making and strategic business actions.
⮚ This process not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports the development of innovative solutions tailored to customer needs.
Visualization: Display real-time information through graphical interfaces
⮚ Customized HMI and SCADA-based visualization solutions are pivotal in modern industrial settings.
⮚ They enable operators to interact with their processes and machinery in real-time, ensuring efficient monitoring and control.
⮚ This integration plays a crucial role in optimizing operations, enhancing safety, and minimizing downtime. Tailoring these systems to specific needs can significantly improve the responsiveness and adaptability of industrial control systems.
Historical Data Logging
⮚ Tailoring to customer needs is essential, especially when it comes to data management. Providing access to historical data is not only crucial for analysis but also for effective troubleshooting.
⮚ By enabling a comprehensive view of past records, businesses can identify trends, make informed decisions, and address issues with precision.
⮚ This approach ensures that the data serves as a valuable resource for ongoing operational excellence and strategic planning.
MIS Reporting
⮚ Management Information System (MIS) reporting is a critical component for organizations to monitor and analyze their operations.
⮚ We have expertise in development of MIS report where we aggregate data from various departments, providing key insights into performance, operations, and activities.
⮚ These reports are essential for management to make informed decisions, often including visual representations like charts and graphs for clarity. Regularly generated, they can be customized for different management levels, ensuring that decision-makers have the most relevant and up-to-date information at their disposal.
21CFR Part 11 compliant SCADA & HMI Programming
⮚ 21CFR Part 11 compliance is crucial for SCADA and HMI programming in industries regulated by the FDA, such as pharmaceuticals.
⮚ Our team has expertise in process and equipment automation where we are ensuring compliance with regulations that mandate the trustworthiness and reliability of electronic records and signatures.
⮚ Implementing robust features such as audit trails, user management functionalities, and secure data storage and retrieval systems is essential.
⮚
These features safeguard against data tampering and uphold the integrity of electronic records, making them as reliable as their paper counterparts throughout their lifecycle.












![panel-01[1] panel-01[1]](https://eleetpro.com/wp-content/uploads/elementor/thumbs/panel-011-qzet7wibzvxnan2llc3lbke7tcjsob95xaavd6zpug.png)


